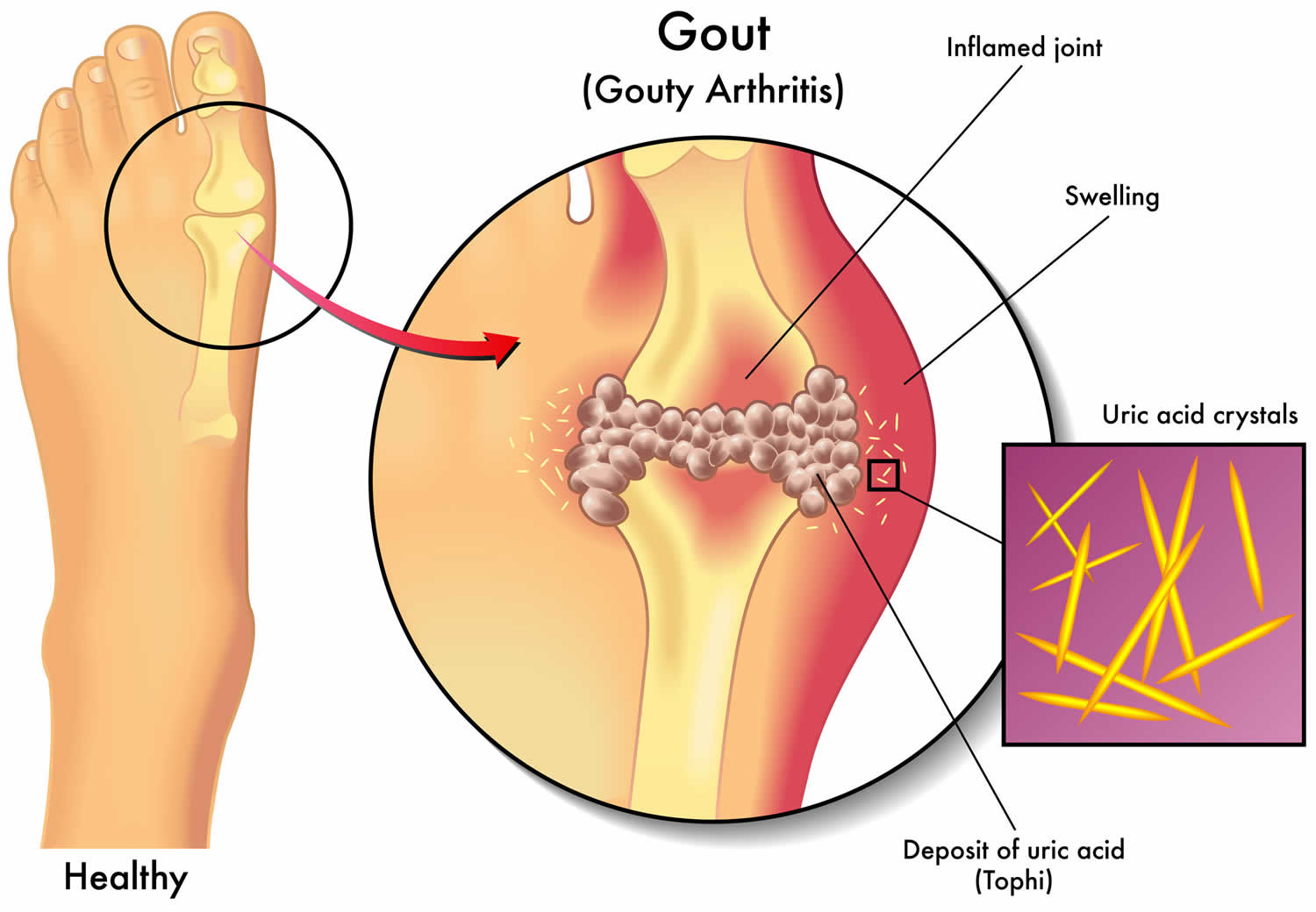
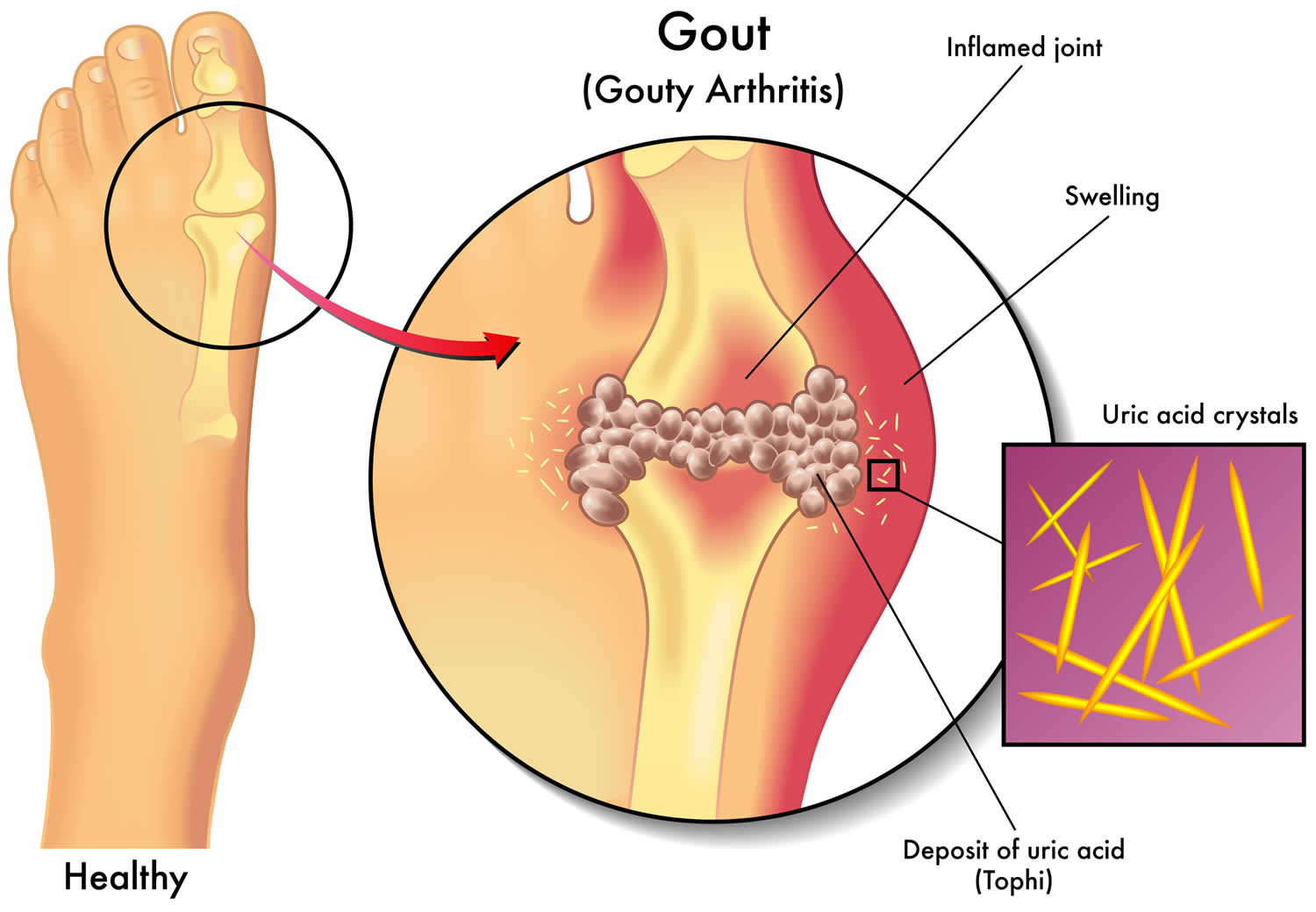
Understanding the Stages of Gout: A Comprehensive Overview
Gout, a form of inflammatory arthritis, is characterized by sudden and severe attacks of pain, redness, and swelling in the joints. It is caused by the accumulation of urate crystals in the joints, leading to inflammation and discomfort. The progression of gout can be categorized into several distinct stages, each with its own set of symptoms and implications for the individual’s health.
1. Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia:
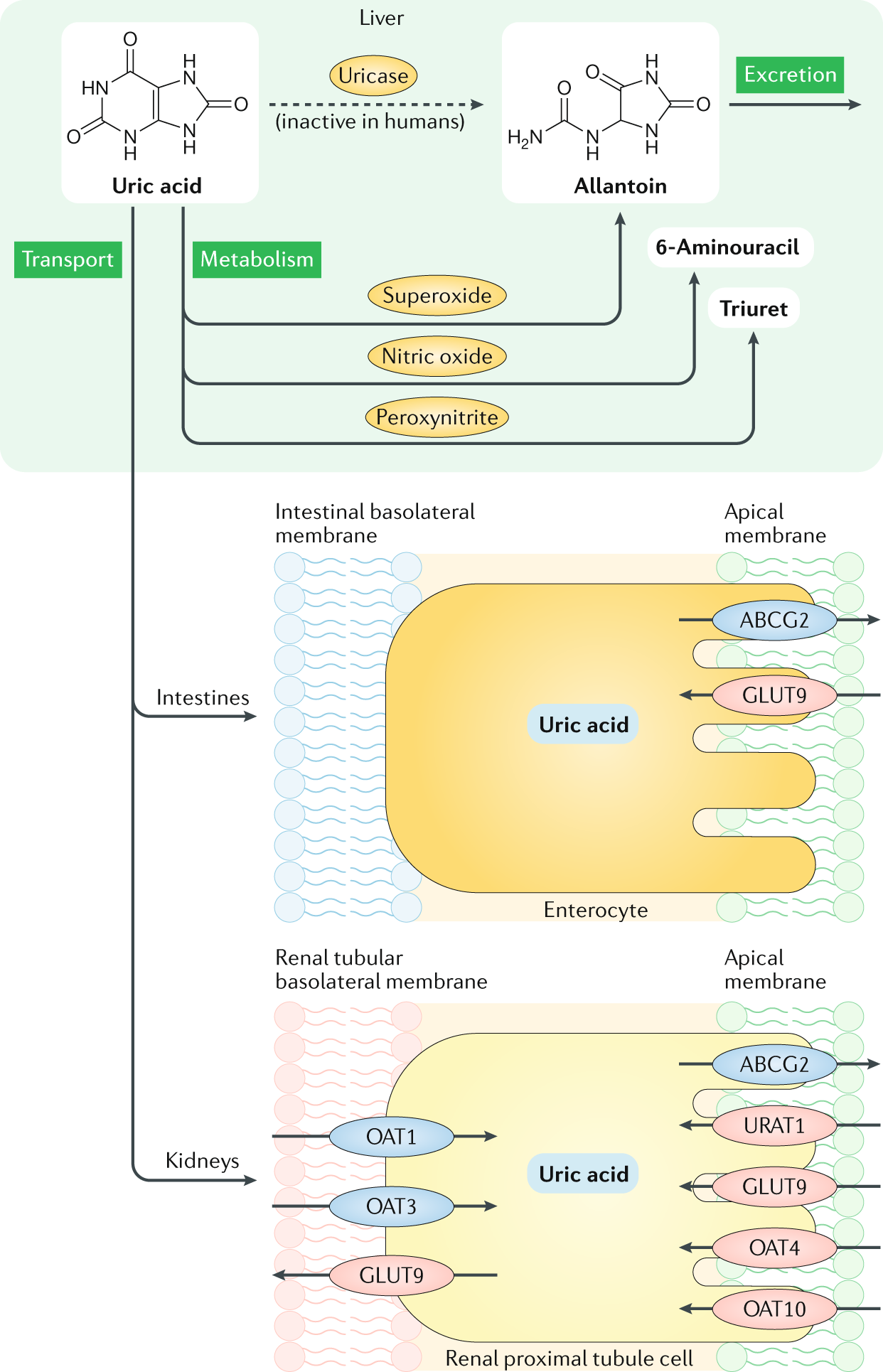
In the initial stage, individuals may have elevated levels of uric acid in their blood, a condition known as hyperuricemia, without experiencing any noticeable symptoms.
Despite the absence of symptoms, the presence of high uric acid levels increases the risk of urate crystals forming in the joints over time.
2. Acute Gout (Gout Attack):
The hallmark of acute gout is the sudden onset of intense pain, swelling, and redness in a joint, often the big toe.
Gout attacks can be triggered by factors such as diet, alcohol consumption, dehydration, and certain medications.
The pain is usually at its peak within 24 hours, making movement and even the touch of a bedsheet excruciating.
3. Intercritical Period:

Following an acute attack, individuals enter an intercritical period characterized by the absence of symptoms.
During this phase, the affected joint returns to normal, and the person may resume their regular activities.
It is important to note that the absence of symptoms does not signify the resolution of the underlying issue.
4. Chronic Gout:
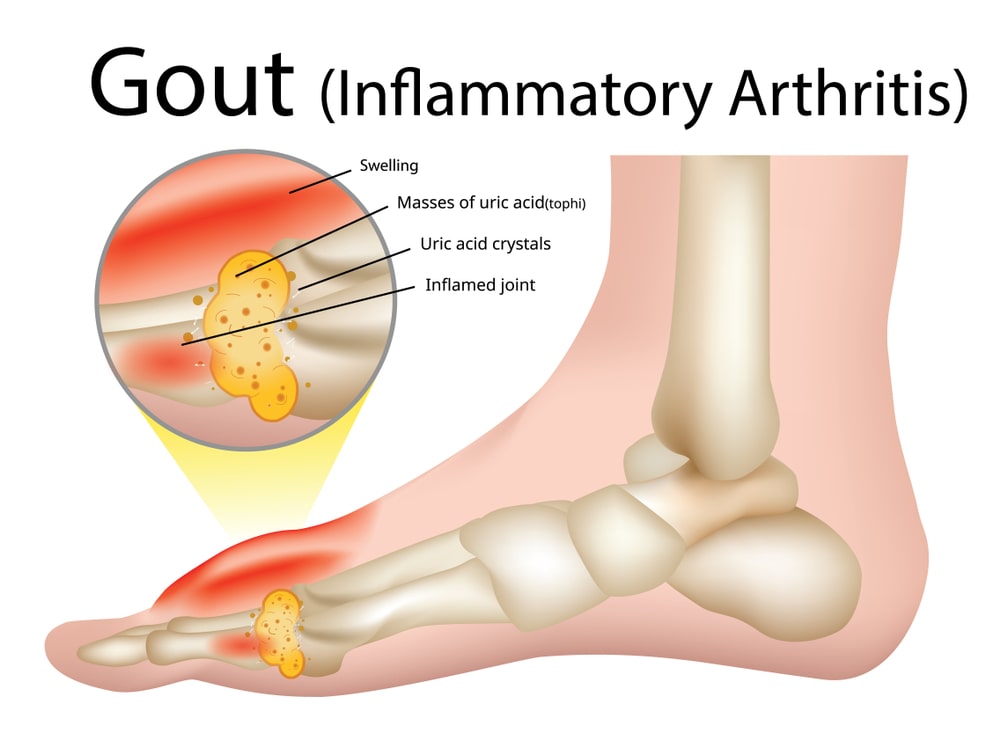
If left untreated, gout can progress to the chronic stage, where individuals experience recurrent gout attacks and persistent joint damage.
Chronic gout is marked by the presence of tophi, which are lumps of urate crystals that accumulate beneath the skin and in joints.
Tophi can cause deformities, joint destruction, and contribute to long-term disability.
5. Advanced Gout:
In advanced stages, gout can lead to complications such as kidney stones, kidney damage, and joint deformities.
Chronic inflammation may affect multiple joints, further diminishing the individual’s quality of life.
Medical intervention, lifestyle modifications, and ongoing management become crucial at this stage to prevent further complications.
Management and Prevention:
Medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and urate-lowering drugs, are commonly prescribed to manage symptoms and prevent future attacks.
Lifestyle changes, including a balanced diet, limited alcohol intake, and maintaining a healthy weight, play a crucial role in preventing gout episodes.
Regular monitoring of uric acid levels and adherence to prescribed medications are essential in controlling the progression of the disease.
Understanding the stages of gout is vital for effective management and prevention. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals affected by this painful condition.