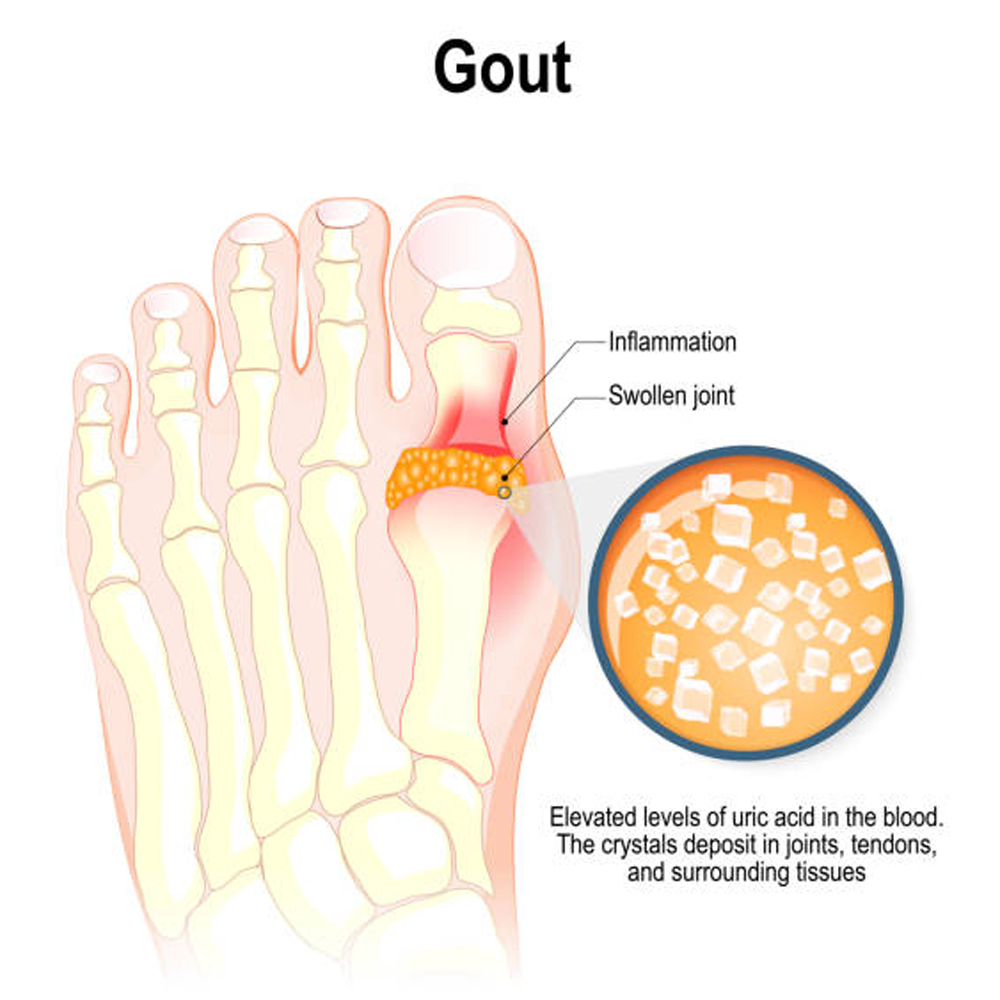
Unraveling the Roots of Gout: Understanding the Causes
Introduction:
Gout, a form of arthritis, has been a persistent and painful ailment affecting individuals worldwide. To effectively tackle this condition, it’s imperative to delve into its origins. This article aims to shed light on the causes of gout, providing insights into the factors that contribute to the development of this inflammatory joint disorder.
1. Uric Acid Accumulation:

At the heart of gout lies the accumulation of uric acid in the body. Uric acid is a byproduct of the breakdown of purines, substances found in certain foods and body tissues. When the body produces too much uric acid or if the kidneys cannot efficiently eliminate it, urate crystals form, triggering inflammation in the joints.
2. Dietary Influences:

Diet plays a pivotal role in the development of gout. Foods rich in purines, such as red meat, organ meats, seafood, and certain vegetables, contribute to elevated uric acid levels. Excessive consumption of these purine-rich foods can tip the balance, leading to the formation of urate crystals and the onset of gout symptoms.
3. Lifestyle Factors:

Several lifestyle factors are associated with an increased risk of gout. Heavy alcohol consumption, particularly beer and spirits, is a known contributor. Alcohol interferes with the body’s ability to excrete uric acid, exacerbating the risk of gout attacks. Additionally, obesity and a sedentary lifestyle are linked to higher uric acid levels, making weight management and regular physical activity essential in preventing gout.
4. Genetic Predisposition:
Genetics also plays a role in gout susceptibility. Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to inefficiently process and eliminate uric acid, putting them at a higher risk of developing gout. Understanding one’s family medical history can provide valuable insights into individual risk factors.
5. Medical Conditions:
Certain medical conditions contribute to the development of gout. Hypertension, diabetes, and chronic kidney disease are known to be associated with elevated uric acid levels. Managing these underlying health conditions is crucial in preventing and controlling gout.
Conclusion:
In summary, the causes of gout are multi-faceted, encompassing dietary choices, lifestyle factors, genetic predisposition, and underlying medical conditions. Recognizing these contributors is pivotal in developing effective strategies for prevention and management. By addressing the root causes of gout, individuals can take proactive steps to mitigate the impact of this painful condition and improve their overall quality of life.